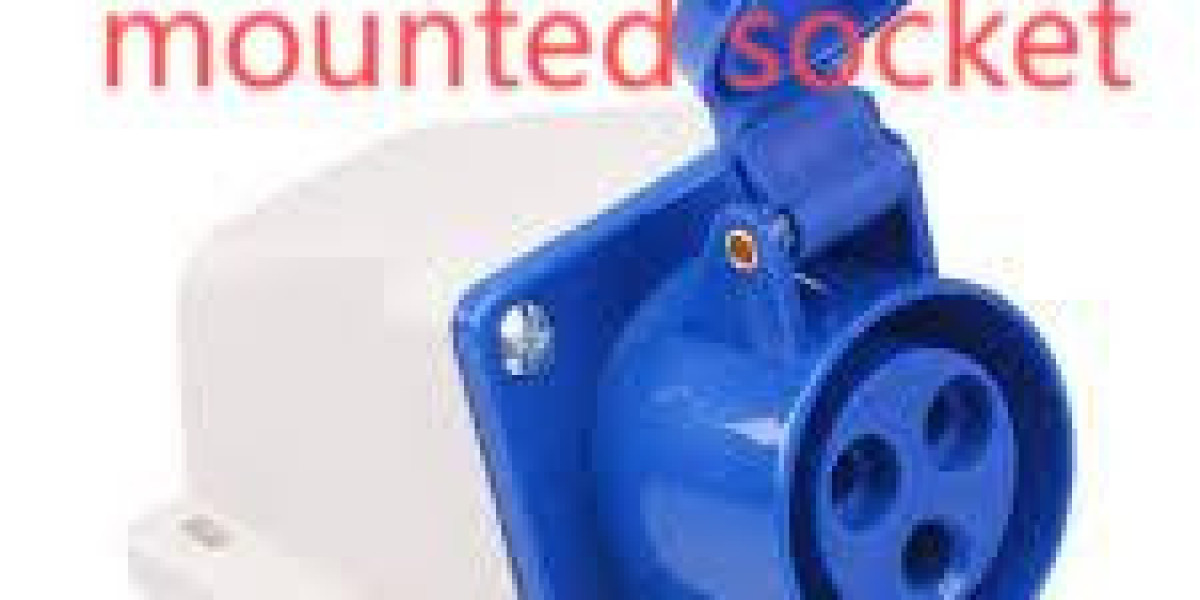
On busy production lines, engineers often install a Industrial surface mounted socket midway along benches to shorten cable runs and reduce hazards for operators, and maintenance teams prefer a Industrial surface mounted socket that offers easy access for inspections, clear labeling, and replaceable modules so repairs are predictable and fast. When placement, product choice, and an actionable maintenance plan align, surface-mounted sockets become reliable service points instead of recurring failure sources.
Site-specific placement and human factors
Before specifying a unit, walk the floor and note how people actually move and use power. Mounting height, sightlines for LEDs or labels, and proximity to mobile equipment affect both safety and service speed. Place sockets where cords won’t cross aisles and where technicians can reach connections without ladders. Consider ergonomic grips and recesses that prevent accidental snags. A placement strategy that minimizes extension-cord use and reduces trip risks pays back immediately in fewer incidents and faster daily operations.
Materials, sealing, and environmental ratings
Choose housings and gaskets that match the operating environment. UV-stable polymers resist cracking outdoors, while stainless steel or powder-coated metal bodies resist impact and chemical exposure in harsh shops. Specify IP ratings appropriate to washdown or dusty conditions and check IK impact ratings if carts or tools may strike the box. Gasket chemistry matters — select compounds whose compression set and chemical resistance suit the site’s cleaning agents and temperature swings. These choices prevent premature aging and preserve ingress protection over repeated service cycles.
Nante modular integration and spare-part strategy
Modular interiors shorten downtime. Favor designs that accept removable mounting plates, DIN-rail inserts, and swappable outlet modules so a single failed component can be replaced without disturbing adjacent circuits. Standardized spare kits — containing common inserts, gaskets, and glands — reduce the variety of parts technicians must carry. Require suppliers to publish compatibility matrices so replacements remain interchangeable across product revisions. A compact spare-part strategy turns most service calls into single-visit repairs, saving labor and avoiding production stops.
Wiring discipline, strain relief, and electrical safety
Many long-term faults originate at the terminals. Use correct conductor sizes, ferrules for stranded wires, and follow published torque specs for terminals and glands. Route cables with strain reliefs to prevent flex-loading on connections, and separate power from control or signal wiring to minimize interference. Provide clear labeling and wiring diagrams inside or adjacent to the box so technicians can quickly trace circuits. When appropriate, integrate local surge protection and isolation features to protect sensitive equipment and simplify troubleshooting.
Thermal management and load planning
Even small enclosures can trap heat; plan accordingly. Locate power-dissipating devices away from sensitive electronics and use thermally conductive mounting plates where heavy loads are present. For continuous high-current applications, oversize conductors and contact areas to limit temperature rise. Periodic infrared surveys during commissioning can reveal hotspots and uneven load distribution. If the site experiences temperature extremes or large load swings, consider simple thermal monitoring to warn of emerging problems before they escalate.
Mechanical mounting and tamper resistance
Secure mounting prevents loosening under vibration and deters casual tampering. Use substrate-appropriate anchors and consider vibration-damping pads in areas with heavy machinery. For public or semi-public installations, add lockable lids or tamper-resistant fasteners. When aesthetics are important, select finishes that match surroundings while still providing required protection. Hidden anchor points and recessed fasteners can deter theft without compromising service access for authorized personnel.
Inspection routines and predictable maintenance
A brief, repeatable checklist reduces surprises: inspect gaskets for compression set, verify gland torque, check for corrosion or discoloration on contacts, and measure contact resistance on critical circuits. Schedule checks after severe weather or heavy use periods. Maintain a log of part replacements and anomalies to build lifecycle forecasts that support budgeting and procurement. Keeping a compact local spare kit and a clear service procedure helps technicians resolve most issues quickly.
Planning for upgrades and future needs
Reserve space and mounting points for potential additions such as surge protectors, monitoring sensors, or extra circuits. Selecting a product family with a consistent footprint across models simplifies later upgrades and reduces the need for enclosure replacement. Consider modest IoT-ready sensors that report temperature, humidity, or lid-open events — these can turn passive sockets into proactive assets that notify teams of failing seals or unusual thermal conditions.
When placement, specification, installation discipline, and a compact spare strategy are combined, industrial surface-mounted sockets become dependable, low-maintenance service points that support productivity rather than hinder it. For product specifications, accessory options, and installation guides, visit www.nante.com