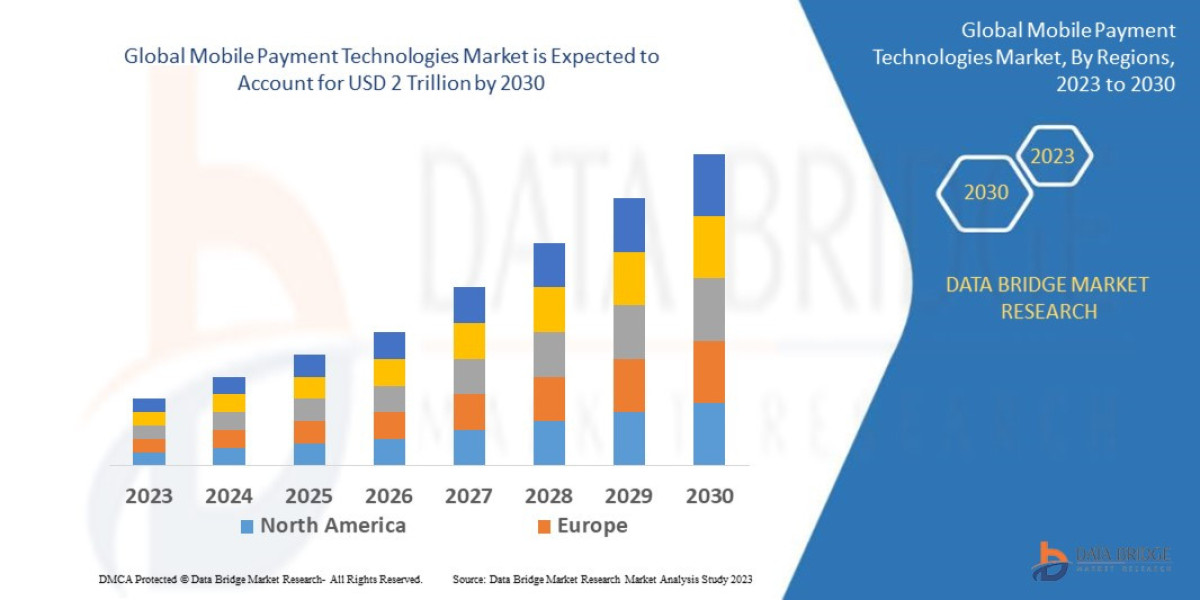
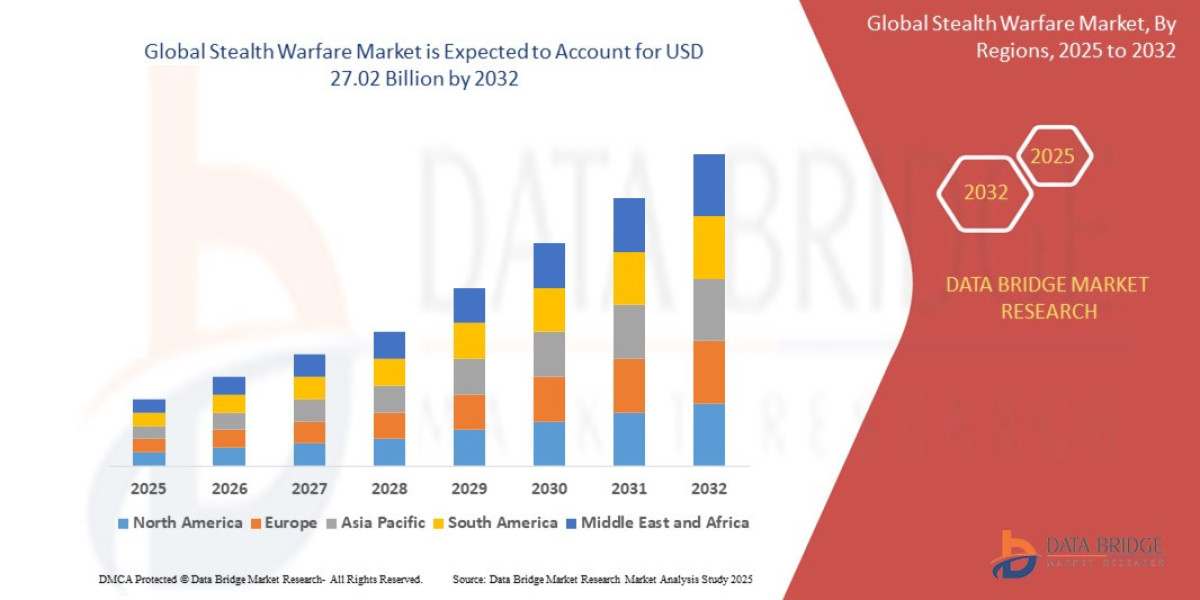
Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Accurate evaluation of the functional significance of coronary stenosis is essential to guide revascularization strategies. Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) provides an objective, physiologically based assessment of coronary blood flow, distinguishing lesions that require intervention from those suitable for conservative management. Its integration with advanced imaging and catheterization technologies has transformed interventional cardiology practices globally.
Understanding Fractional Flow Reserve
Fractional Flow Reserve is defined as the ratio of the maximum achievable blood flow in a stenotic artery to the maximum flow in a hypothetical normal artery. Measured during coronary angiography using a specialized pressure wire, FFR helps cardiologists determine the hemodynamic impact of coronary lesions.
Key benefits of FFR include:
Precise identification of ischemia-causing lesions
Avoidance of unnecessary stenting or bypass procedures
Improved clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness
FFR measurements typically guide percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI), optimizing patient-specific treatment plans.
Fractional Flow Reserve Procedure
The standard FFR procedure involves:
Catheterization: Insertion of a guide catheter via radial or femoral artery
Pressure Wire Placement: A specialized FFR wire is positioned across the coronary lesion
Vasodilation: Administration of a hyperemic agent (e.g., adenosine) to maximize blood flow
Pressure Measurement: The FFR value is calculated by comparing distal coronary pressure to aortic pressure
FFR values ≤0.80 generally indicate significant ischemia, warranting revascularization. The procedure is safe, minimally invasive, and associated with low complication rates.
Fractional Flow Reserve CT (FFR-CT)
FFR-CT is a non-invasive technology that uses computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA) combined with computational fluid dynamics to estimate FFR values. Advantages include:
Avoidance of invasive catheterization
Rapid assessment of coronary lesions
Integration with routine coronary CT scans for comprehensive evaluation
FFR-CT is particularly valuable in patients with intermediate coronary stenosis or when invasive angiography carries higher risk. It complements traditional FFR by enhancing diagnostic confidence and reducing unnecessary interventions.
Fractional Flow Reserve Machines and Devices
FFR measurements rely on advanced cardiovascular devices:
Pressure Guide Wires: Equipped with sensors to measure distal coronary pressure
FFR Measurement Systems: Monitors and software that calculate real-time FFR values
FFR-CT Platforms: Cloud-based or on-site computational solutions for non-invasive analysis
Technological improvements focus on enhancing accuracy, reducing procedure time, and improving user interface for interventional cardiologists.
New Technologies and Innovations
Recent developments in FFR technology include:
Wireless Pressure Sensors: Minimizing procedural complexity and enhancing mobility
Integration with Intravascular Imaging: Combining FFR with IVUS or OCT for anatomical and functional assessment
AI and Computational Modeling: Improved predictive analytics for FFR-CT
Robust Software Platforms: Streamlined workflow for clinical decision-making and reporting
These innovations improve procedural efficiency, reduce radiation exposure, and enhance patient safety.
Market Trends and Growth Drivers
The FFR market is growing due to increasing prevalence of CAD, rising adoption of minimally invasive cardiology techniques, and technological innovation. Key trends include:
Expansion of FFR-CT adoption in non-invasive diagnostics
Rising demand for patient-specific, data-driven interventions
Increasing investments in advanced cardiovascular devices
Integration of AI and cloud computing in cardiovascular imaging
North America and Europe lead the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, while Asia-Pacific is emerging as a high-growth region driven by rising CAD prevalence and healthcare modernization.
Conclusion
Fractional Flow Reserve is transforming the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease by providing precise, physiologically relevant data. Innovations in FFR procedures, FFR-CT, and device technologies are enhancing accuracy, safety, and accessibility. As adoption grows globally, FFR is set to remain a cornerstone of modern interventional cardiology, improving outcomes and optimizing patient care.
Related Reports
· Endometriosis treatment Market
· Neuromodulation Devices Market
· Hospital Information System Market