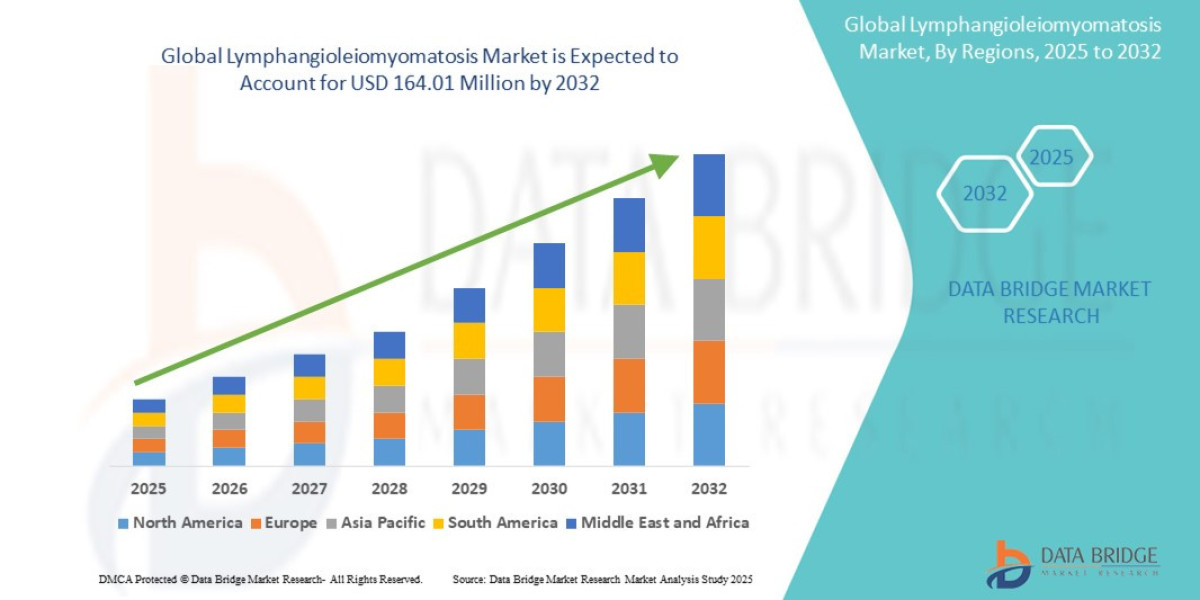
As Per Market Research Future, the Solid Waste Management Industry is evolving rapidly, characterized by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on waste collection and processing services. This industry encompasses a variety of services aimed at managing solid waste effectively, including recycling and landfill operations. The increasing focus on environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance is driving innovation within the industry. As companies invest in research and development to improve waste management practices, the solid waste management industry is likely to witness substantial growth.
The solid waste management industry has become increasingly crucial in modern urban development and environmental sustainability. With rapid urbanization, industrialization, and population growth, the generation of waste has risen exponentially, creating the need for effective management strategies. Solid waste management encompasses the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and disposal of solid waste. It plays a pivotal role in public health, environmental conservation, and resource recovery. Governments, private organizations, and communities are now prioritizing sustainable waste management systems to reduce environmental pollution and promote circular economy practices.
Key Drivers of the Industry
Several factors are driving the growth of the solid waste management industry. Increasing population and urbanization are generating higher amounts of municipal and industrial waste. Rising awareness about environmental pollution and stringent government regulations are encouraging investments in advanced waste management technologies. Additionally, growing initiatives for recycling and waste-to-energy projects are creating new revenue streams for the industry. Technological advancements such as smart waste bins, GPS-enabled collection vehicles, and automated sorting systems are enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. The integration of digital solutions, including data analytics and IoT, is also transforming waste management into a more efficient and sustainable process.
Challenges Faced by the Industry
Despite the opportunities, the industry faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the high cost associated with waste collection, transportation, and treatment infrastructure. In many developing regions, improper segregation of waste at the source hampers recycling efforts and increases landfill pressure. Moreover, regulatory compliance, labor shortages, and lack of awareness in rural areas pose significant hurdles. The management of hazardous and biomedical waste requires specialized treatment methods, which adds complexity and operational costs. Additionally, public resistance to waste processing plants and incineration facilities can create social challenges, limiting the expansion of the industry.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
The solid waste management sector is witnessing a wave of innovation. Waste-to-energy plants are gaining traction, converting non-recyclable waste into electricity or heat, thereby reducing landfill dependency. Advanced recycling technologies are enabling the recovery of valuable materials like plastics, metals, and paper. AI-driven sorting systems and robotics are improving the efficiency and accuracy of material recovery facilities. Furthermore, the concept of zero-waste cities is being promoted, emphasizing waste reduction at the source and promoting circular economy principles. Mobile applications and smart sensors are helping citizens actively participate in recycling and waste segregation initiatives, leading to more sustainable urban ecosystems.
Market Outlook and Opportunities
The solid waste management industry is expected to grow steadily over the next decade. Increasing government funding for urban sanitation, stricter environmental regulations, and rising private sector investments are fueling market expansion. Emerging economies with growing urban populations represent significant opportunities for waste management service providers. Collaboration between municipalities, private enterprises, and technology providers is creating innovative models for efficient waste collection, treatment, and recycling. Additionally, sustainability-driven consumer preferences are creating demand for eco-friendly packaging and biodegradable materials, indirectly influencing the solid waste management ecosystem.
Environmental and Social Impact
Effective solid waste management contributes to environmental conservation by reducing landfill usage, preventing soil and water contamination, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Recycling initiatives reduce the need for raw material extraction, conserving natural resources. On a social level, proper waste management ensures public health safety by preventing disease outbreaks and promoting cleaner living environments. Community engagement programs and awareness campaigns are fostering responsible waste disposal practices among citizens, creating a culture of sustainability that aligns with global environmental goals.
Conclusion
The solid waste management industry is evolving into a critical sector for sustainable development and urban planning. With technological innovations, regulatory support, and increasing environmental awareness, the industry is poised for growth. Addressing challenges such as infrastructure costs, public resistance, and hazardous waste management will be key to unlocking its full potential. As cities and industries adopt smarter and greener solutions, solid waste management will continue to play a vital role in shaping cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable communities worldwide.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main types of solid waste?
Solid waste includes municipal waste, industrial waste, biomedical waste, e-waste, and hazardous waste. Municipal waste consists of household and commercial refuse, while industrial waste originates from manufacturing activities. Biomedical waste includes medical and healthcare-related materials, and e-waste comprises discarded electronic devices.
Q2: How does waste-to-energy technology work?
Waste-to-energy technology converts non-recyclable waste into electricity or heat through processes like incineration, pyrolysis, or anaerobic digestion. This helps reduce landfill usage while generating renewable energy.
Q3: What role does recycling play in solid waste management?
Recycling reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills, conserves natural resources, and lowers environmental pollution. Advanced recycling technologies enable the recovery of valuable materials like plastics, metals, and paper for reuse in production.
More Related Reports:
Residential Fan Coil Convector Market Analysis
Dry Ice Blasting Machine Market Analysis